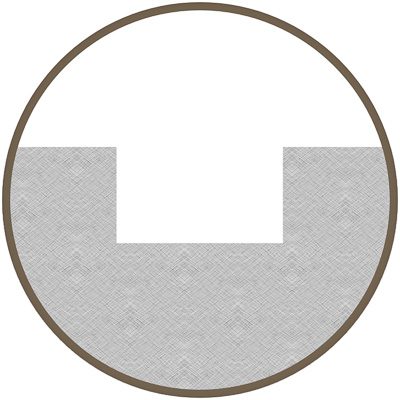
Laser Engraving / Evaporation
Engraving creates high heat when marking, which causes the material to vaporize. Since surface material is removed, there is very little damage to the material itself (compared to laser etching), but this method may not be appropriate for marking safety critical parts. The resulting mark is the same as chemical etch mark, and it is the fastest way to mark with a laser.
- Vaporization of base material sufficient to produce depth required, typically from .0001″ to .005″
- Vaporization process identical to surface etching
- Create deeper marks with several repeated passes
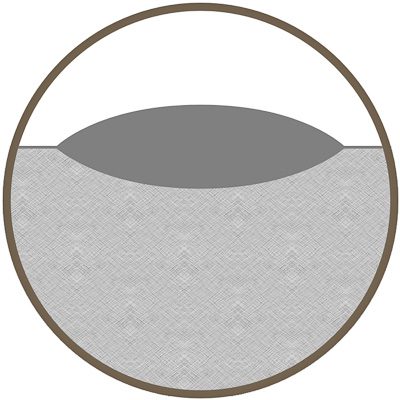
Laser Etching / Melting
Etching occurs when the heat of the laser beam causes the surface of the material to melt. The melted material expands, causing a raised mark. Also referred to as melting or foaming.
- Changes the surface finish of metal, thus altering its reflectivity and enhancing contrast
- Penetration depth is typically no more than .0001″ deep
- Considerable speed advantage because the material is almost instantly vaporized with each pulse, allowing the beam velocity to be set as high as possible, while still maintaining desired depth and acceptable pulse overlap
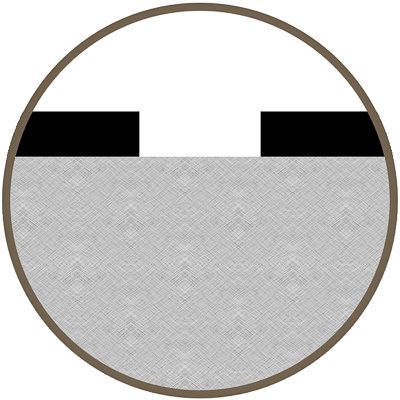
Laser Ablation
Ablation is the process of engraving a surface coating. This method creates excellent contrast without affecting the underlying material.
- Works with coatings, paint, or other surface treatments
- Typically used for marking anodized aluminum, backlit buttons, and painted steel
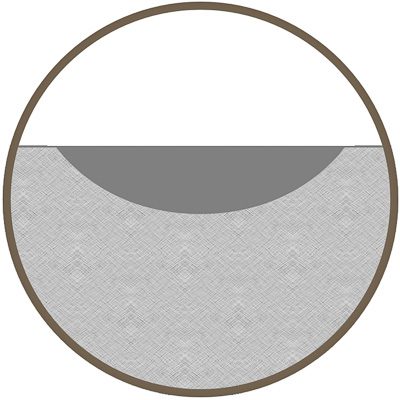
Laser Coloration / Annealing
Coloration is achieved by moving a low-power laser beam slowly across the material. This method causes discoloration for high-contrast marks without disrupting the material surface. Also referred to as charring (plastics) and annealing (metals).
- Draws carbon and/or oxides from the base metal material to get a contrasting mark
- Applies comparatively low temperatures to metal to anneal the surface
- Marking beam will produce a sharp contrasting line to the surrounding area with little or no penetration
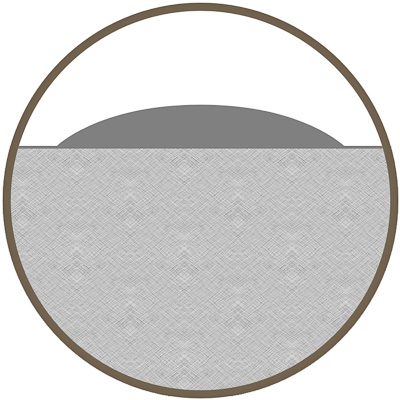
Laser Bonding
Laser bonding is a process where pigments or other coatings are applied to the material and then bonded to the surface by the heat generated with the laser. Safe for use on safety critical parts, the marks are heat resistant and unaffected by fluids or salt.
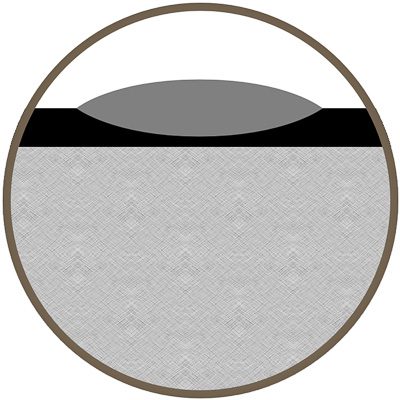
Laser Coat & Mark
This process is used when the surface of the material cannot be subjected to damage or alteration from the laser. Here the surface of the material is coated, and the coating is then etched.
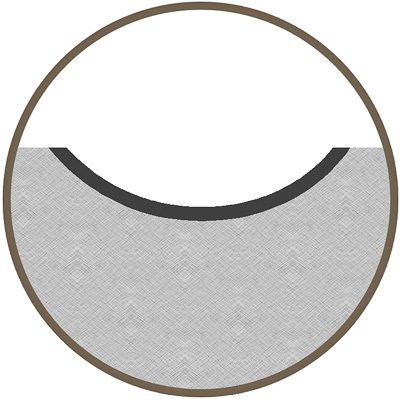
Engrave & Melt
Material removal and surface melt, common in marks requiring lifetime readability in a demanding environment.
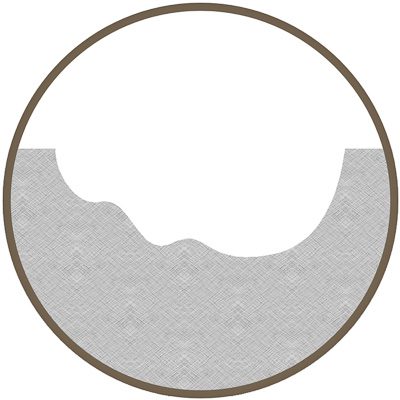

3D Engraving
- Ability to mark 3-dimensional graphics using optional software package
- Creates extremely high quality 3D marks at significant depths in a fraction of the time
